ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE: PREVENTING ESD DAMAGE IN CLEANROOM SETTINGS
What is Electrostatic Discharge?
Electrostatic Discharge, caused by static electricity, is the release of electricity when two differently charged objects come into contact. It can also come from environmental conditions, such as exposure to light, heat and cooling.
Some familiar examples of ESD that we experience are the shock we receive after walking across a carpet and touching a metal doorknob, or, rubbing a ballon to cause hair to stand on end. We also see static electricity in larger forms too, such as the strike of lightning. ESD also occurs in less dramatic forms which may be neither seen nor heard, yet still be large enough to cause damage to sensitive electronic devices.

This poses a challenge for industries that require Cleanroom environments. It can result in slow production, attraction of contaminants and can create safety issues.
When the ESD transfers onto an electronic device, the intense heat can melt, vaporise, or otherwise damage the intricate parts of the device. This damage can cause it to fail.
It is essential that precautions be taken prevent such damage taking place.
Managing and Preventing Electrostatic Discharge
Electrostatic Discharges can occur without warning. Prevention requires an understanding of the environment in which an electronic device is manufactured, handled, and used.
Some examples of ESD preventative measures include the following.
Using flooring, devices, chairs, and other furnishings that are safe against Electrostatic Discharge.
Making the correct choice of floor system withing an EPA (Electrostatic Protected Area) is essential to providing adequate protection from the harmful effects of ESD. Such flooring will have a special coating that safely dissipates electrostatic charge to the ground, faster than it accumulates.
There is also the option of using ESD protective mats, which work the same way as ESD safe flooring, but do not cover such a vast area.
Likewise, chairs and other Cleanroom furnishings can be obtained that are designed to protect against and control the build up of static charge.
Such furnishings must comply to European Standard BS EN 61340-5-1:2016 - Protection of Electronic Devices from Electrostatic Phenomena.
Cleanroom Supplies stock a variety of ESD chairs, including one with the addition of a HEPA filter. See the category page here.
Ensure workers wear anti-static clothing and shoe covers.
Anti-static protective clothing can be worn by workers to prevent the occurrence of Electrostatic Discharges. Such garments must be constructed from anti-static materials and must conform to European Standard EN 1149-3 – Electric Discharge.
Establishing Ground Connections
An operator working on an ESD-sensitive device at a workbench can typically generate 6,000-7,000 volts of static charge by simply moving around. It is worth noting that many electronic components can be damaged by less than 1,000 volts. Some can even be damaged by less than 30 volts!
By wearing ESD protection, the operator becomes ‘grounded’ in the sense that all static charge will be dissipated to the Earth.
Protective grounding equipment can come in the form of footwear, wrist straps, cords, or heel straps.
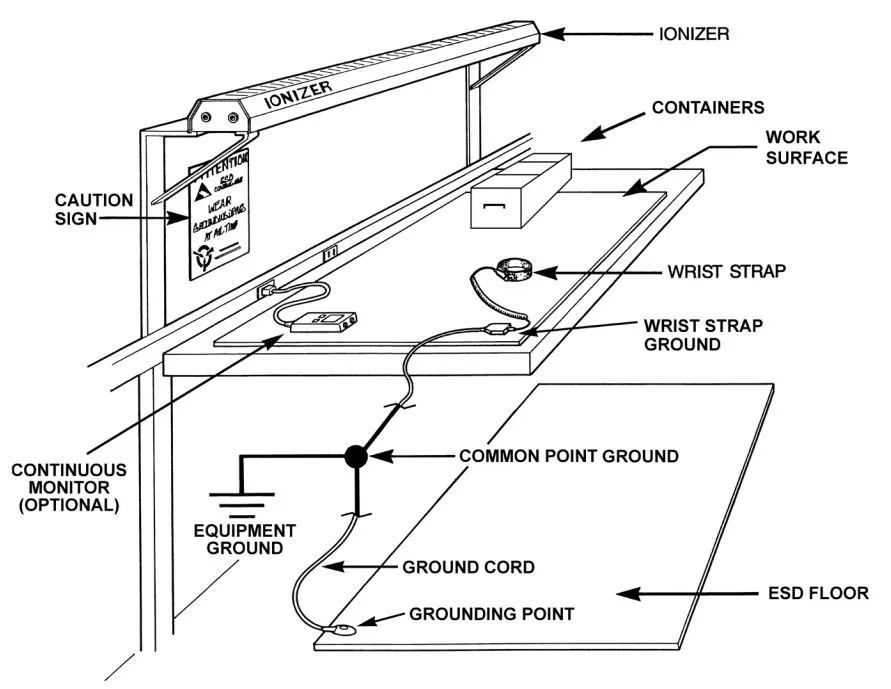
Above Image credited to Desco Europe.
Carefully monitoring the air humidity and temperature within an EPA environment.
The ideal environment for an EPA requires the air humidity to be between 30-50%, and the temperature to be 18-22°C. Cooler, humid air helps to dissipate static charge and prevent a build-up.
Get In Touch
Simply contact our helpful team if you have any questions:
Mail: [email protected]
Tel: 01768 896 800














